InHouse Banking • Definition Gabler Banklexikon

What’s New for InHouse Banking with SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Public Edition 2302 Release SAP Blogs
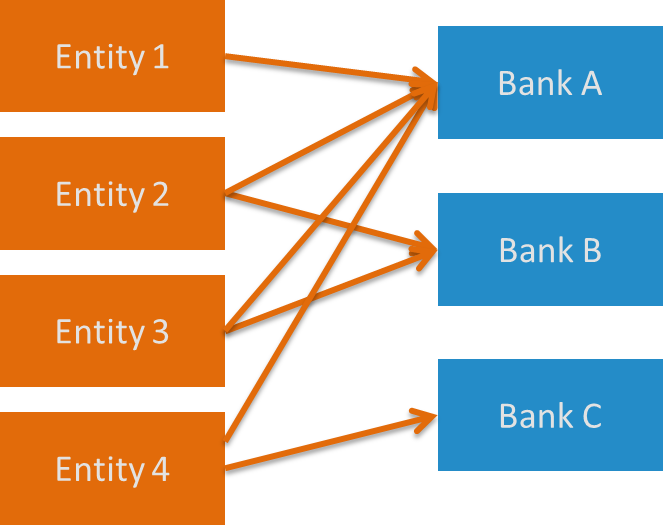
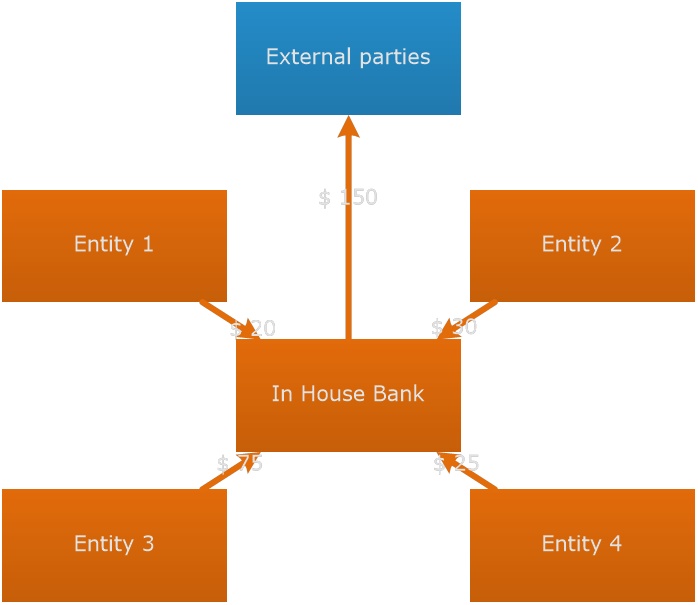
What is In House Bank? The In House Bank (further "IHB") is an internal bank that sits between the entities of the group and the external bank. In this example all entities are dealing with the IHB. The IHB deals with the external bank. So, instead of each entity doing business with the external bank, everything now goes through the IHB.

5 Steps to Successful Build an Inhouse Bank
Their achievements include: Reducing the banking structure in the EMEA from 24+ banks to 6. Reducing the banking structure in North America from 30 banks to a target of 4. 80% of cash is now centralized in the EMEA (up from 55%), making an additional $1 billion+ available in liquidity. 1 SWIFT connection and 6 host-to-host and e-banking systems.
In House Bank (IHB) The workings Treasury Improvement
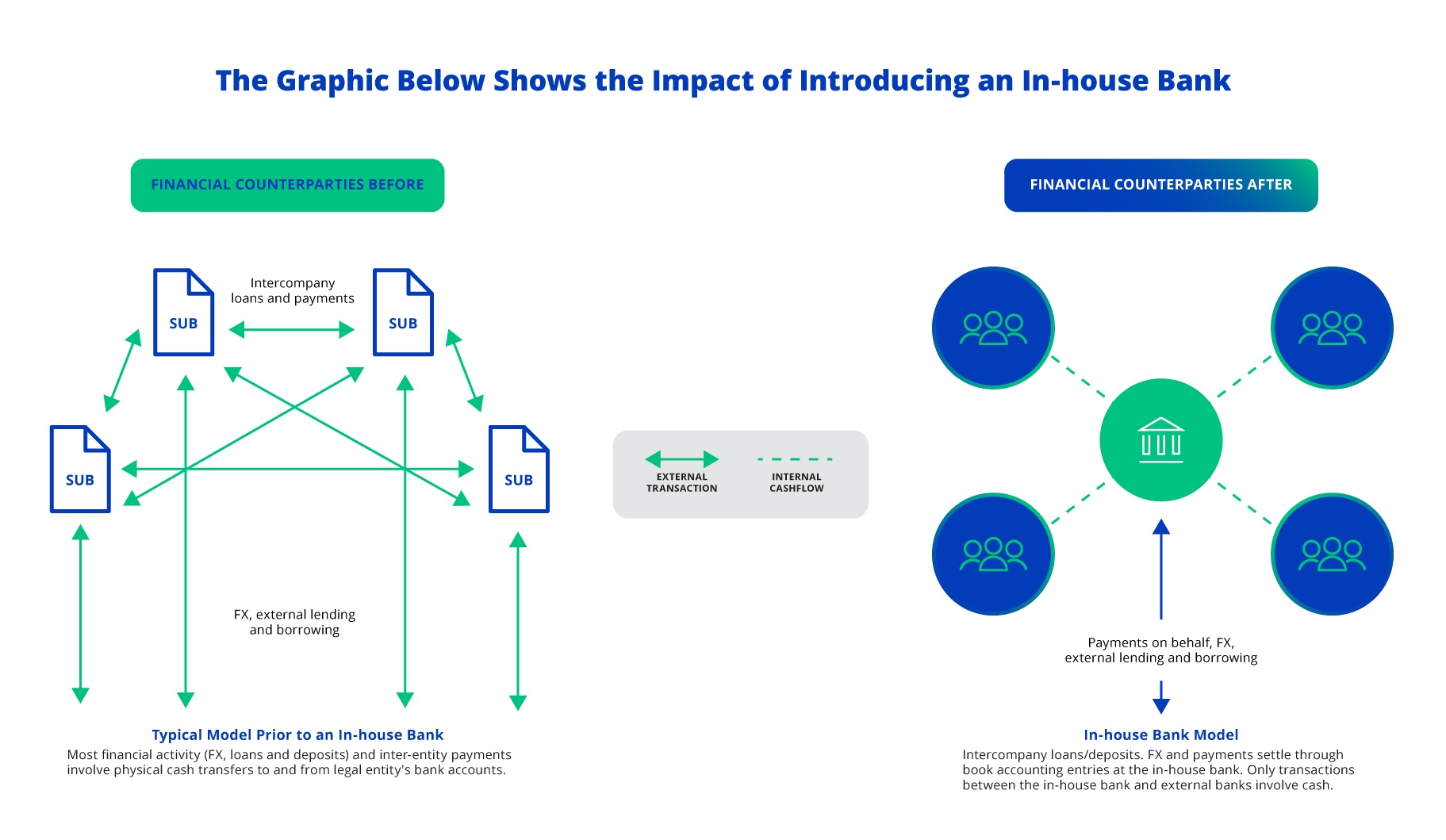
An in-house bank (IHB) is a structure within an organization where a specific entity takes on centralized management of treasury functions, such as cash management, liquidity and risk. Let's look at a few key functions of an in-house bank and how some similar steps could help your organization. Treasury owns corporate cash

What Is an In House Banking Emperor Business
Using your company's own resources for financing, an in-house bank (IHB) is a cost-effective way of consolidating your treasury functions — such as funding, FX and cash management — into one central entity rather than having each subsidiary work through a different local bank.
Top 5 benefits of an Inhouse Bank (IHB)
In an in-house banking model, funds are pooled into a single account from which the treasury can issue transfers and loans. Not only does a centralized account make funds management easier, but it can also generate better investment returns than having multiple subsidiary accounts.
In House Bank (IHB) The workings Treasury Improvement
Top 5 benefits of an In-house Bank (IHB) What is an in-house bank? Why should it be introduced to global organizations? How to implement it? What services can it provide? Find answers in this ebook. What is an in-house bank? Why should it be introduced to global organizations? How to implement it? What services can it provide?

Cómo y por qué usar el homebanking Buenas Inversiones
What is an in-house bank? An in-house bank is a centralized bank that is specifically set up for your organization for centralized, transparent group-level cash management. An in-house bank (also referred to as IHB) provides the following cash management features: Payment hub Manage all internal payments through an in-house bank.
InHouse Banking • Definition Gabler Banklexikon
In-house financing is a type of seller financing in which a firm extends customers a loan, allowing them to purchase its goods or services. In-house financing eliminates the firm's reliance on the.

In house banking Deloitte México
In-house banks (IHBs) and virtual accounts are powerful tools in the treasury space that have historically been more popular outside the U.S. Yet, both of these solutions present opportunities to U.S. treasurers, and form a potent combination that can create big advantages for organizations.

Recorded Webinar 5 Benefits of InHouse Banking Solutions FTI Treasury
What is In House Banking? In simple terms, in-house banking offers an internal or virtual account structure to the group entities, which hold the pulse to replicate the services of the external bank facility.
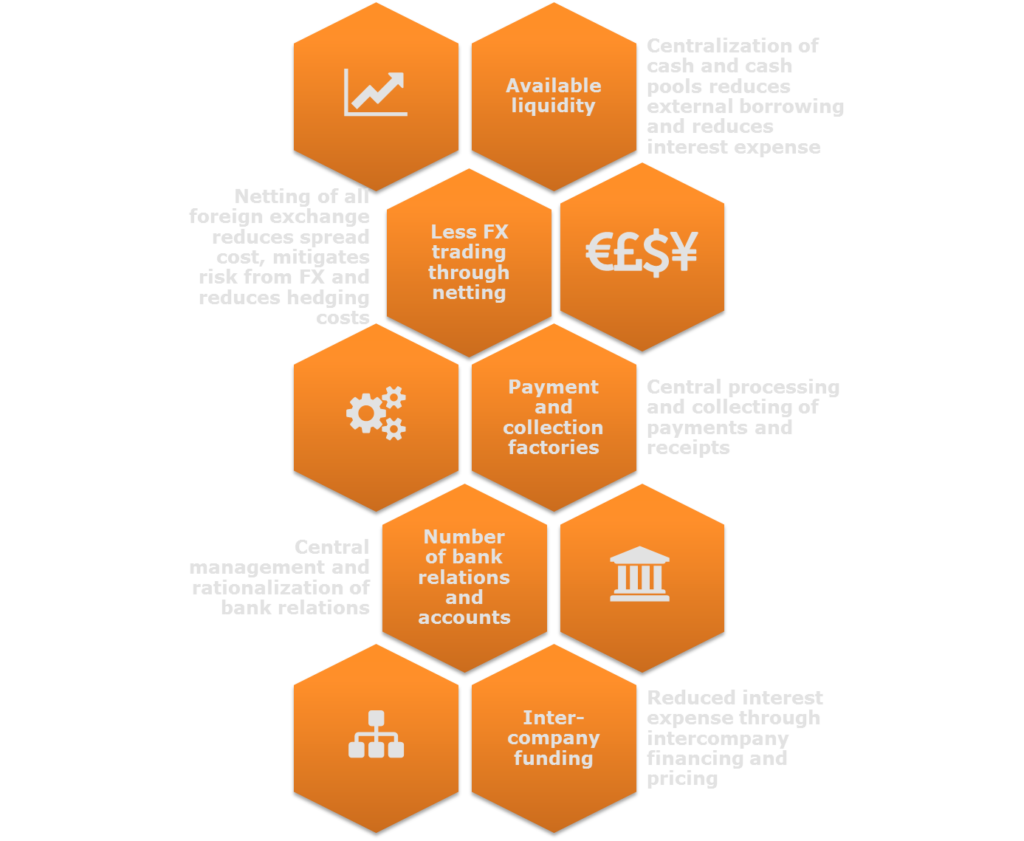
In House Bank (IHB) The workings Treasury Improvement
For many treasurers, creating an in-house bank is an intimidating prospect. But with robust planning, a clear phased approach, and some suitable technology from an experienced partner, it can be easier than you may think, says Jouni Kirjola, Head of Solutions, Nomentia. Corporates that have set up an in-house bank (IHB) often discover greater.

Solutions by use case Inhouse banking Datalog Finance
"An in-house bank can be many things—at one end of the scale, a bank that every subsidiary has to deal with for every transaction, or at the other, an attempt to improve visibility of global cash, exposures and treasury activity while still leaving some autonomy with local entities for local arrangements," said Miranda Hall, director, internatio.
-900pxw.jpg/95937afa-92f1-e8d5-a034-b2a551c189e8?t=1637921222837&imagePreview=1)
Inhouse Banking How does it work? DBS Corporate Banking
In-house banks are most commonly used by large, multinational companies that have complex external bank account relationship structures, large numbers of affiliates within the enterprise, and substantial volumes of both vendor payments and intercompany invoices.

Centralizing Payments with an InHouse Bank Why & How
An in-house bank allows you to lay the foundations for transparent group-level cash management. You can also take care of a variety of other finance and treasury functions centrally, such as banking relationship management, currency risk management, payment and collection management, and internal lending. At the basic level, an in-house bank.

In house Banking A Centralized Treasury Model for Corporates
In-house banking directly contributes to a reduction in the risk of fraud and improvements in cybersecurity. Group entities reduce their external interactions and delegate responsibilities to the company conducting the in-house banking. The operational risk associated with workflow management is concentrated and opportunities for fraud are.

Webinar Trailer Inhouse banking with virtual accounts YouTube
SAP In-House Banking is the new innovation, an internal banking solution, where subsidiaries can maintain in-house bank accounts with headquarters, available from this year, with SAP S/4HANA Cloud 2208 release. It works with both SAP S/4HANA Cloud and on premise with advanced payment management.